How to Choose the Right Urinary Catheter for Different Medical Conditions?
Feb 22,2026
Choosing the right Urinary Catheter is critical for patient safety, comfort, and infection prevention. Healthcare providers, hospitals, and medical equipment distributors must carefully evaluate different types of catheters based on patient conditions, duration of use, and specific medical needs.
Understanding Urinary Catheter Types
Urinary Catheter selection depends on the type, size, material, and intended duration of use. Understanding the differences helps reduce complications and optimize patient care.
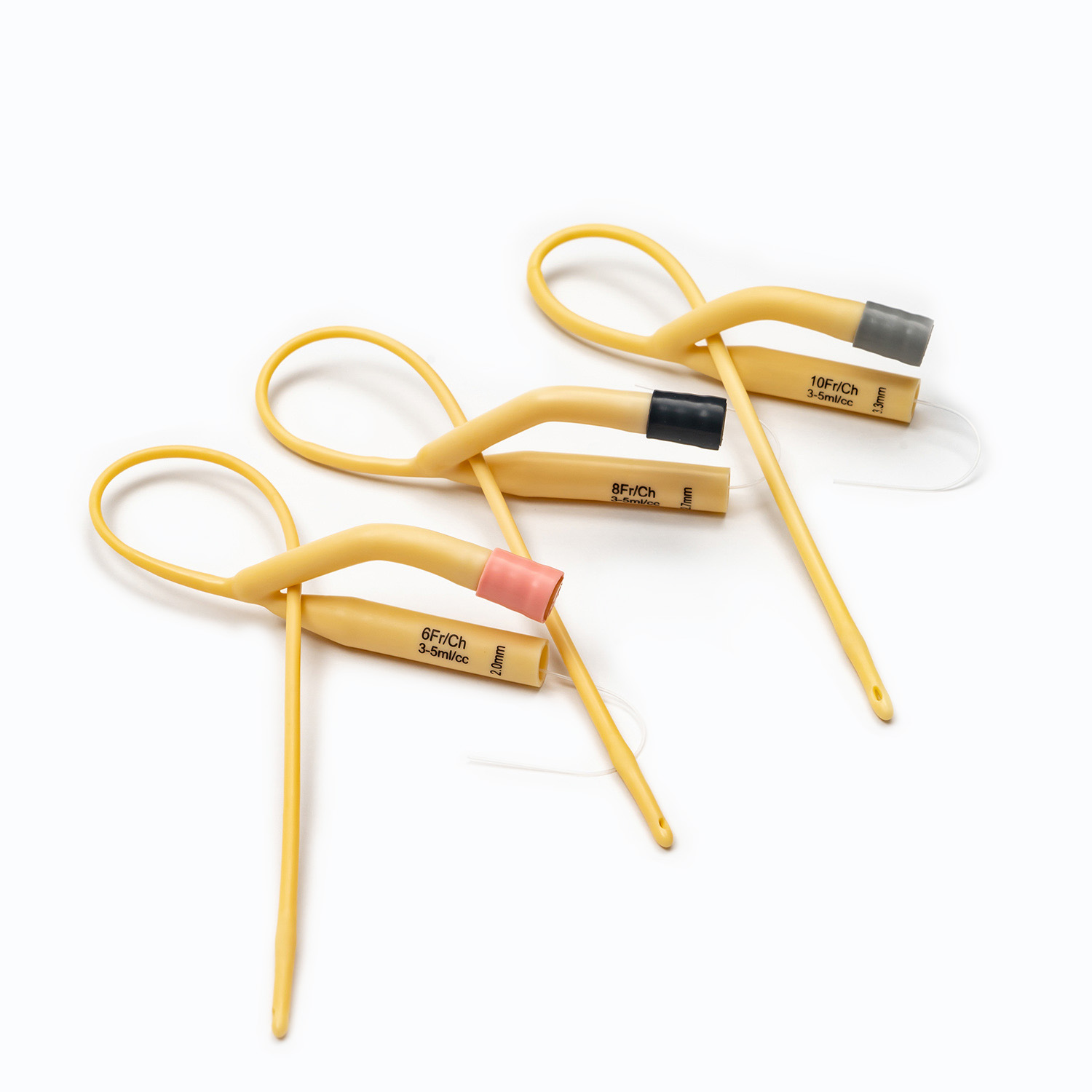
1. Foley Catheter vs. Intermittent Catheter
Foley catheters are designed for long-term use and remain in place, while intermittent catheters are inserted temporarily to drain the bladder.
| Type | Duration | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Foley Catheter | Long-term | Continuous drainage, suitable for immobilized patients | Higher infection risk, requires careful maintenance |
| Intermittent Catheter | Short-term | Lower infection risk, more comfortable for patients | Requires repeated insertion, may cause discomfort |
2. Male vs. Female Catheter
The anatomical differences between male and female patients affect the choice of catheter. Male catheters are longer and designed to reach the bladder through the urethra, while female catheters are shorter.
| Type | Length | Application | Notes |
| Male Catheter | Long | Males requiring bladder drainage | May require lubrication for comfort |
| Female Catheter | Short | Females requiring bladder drainage | Insertion is simpler, lower risk of urethral trauma |
Material Considerations for Urinary Catheter
The material of a Urinary Catheter impacts infection risk, patient comfort, and cost-effectiveness. Common materials include silicone, latex, and PVC.
- Silicone Catheter: Biocompatible, suitable for long-term use, lower risk of encrustation.
- Latex Catheter: More flexible and cost-effective, may cause allergic reactions in sensitive patients.
- PVC Catheter: Economical for short-term use, less comfortable for prolonged catheterization.
Medical Condition-Based Catheter Selection
Different medical conditions dictate the type and duration of catheterization. Proper selection reduces complications and improves patient outcomes.
1. Urinary Retention
Patients with acute or chronic urinary retention often require a Foley Catheter for continuous drainage.
2. Post-Surgical Patients
Short-term catheterization with an Intermittent Catheter is preferred to reduce infection risk and facilitate mobility.
3. Long-Term Care / Chronic Conditions
For patients with chronic conditions, material selection (e.g., silicone) and long-term Urinary Catheter types are essential to minimize encrustation and urinary tract infections.
Technical Considerations and Best Practices
Healthcare facilities and distributors must assess several technical factors:
- Catheter Size (Fr): Size must match the patient’s urethra to prevent trauma.
- Balloon Capacity: Ensure Foley catheters have appropriate balloon volume for retention.
- Lubrication & Insertion Technique: Proper technique reduces urethral injury and infection risk.
- Drainage Bags and Accessories: Compatible drainage systems improve hygiene and monitoring.
Comparative Table for Quick Decision-Making
| Factor | Foley Catheter | Intermittent Catheter | Material Consideration |
| Use Duration | Long-term | Short-term | Silicone preferred for long-term; PVC or latex for short-term |
| Infection Risk | Moderate to High | Low | Silicone lower encrustation, latex may cause allergy |
| Patient Comfort | Moderate | High | Flexible materials increase comfort |
| Maintenance | Requires frequent monitoring | Minimal maintenance | Proper insertion and hygiene are critical |
5 Key FAQs About Urinary Catheter Selection
1. What is the difference between a Foley Catheter and an Intermittent Catheter?
Foley catheters are for long-term continuous drainage, whereas intermittent catheters are used for temporary bladder emptying with lower infection risk.
2. How do I choose the right catheter material for my patients?
Choose silicone for long-term use, latex for short-term flexible applications, and PVC for economical short-term needs. Patient allergies must always be considered.
3. Are there anatomical considerations when selecting a Male Catheter vs Female Catheter?
Yes, male catheters are longer and designed for urethral passage in men, while female catheters are shorter and easier to insert safely.
4. How can healthcare providers reduce infection risk when using Urinary Catheter?
Proper hygiene, selecting the appropriate catheter type and material, correct insertion techniques, and routine monitoring are key to minimizing infections.
5. What factors should B2B purchasers consider when selecting Urinary Catheter products?
Consider catheter type, material, size, intended duration, patient demographics, and regulatory compliance. Technical compatibility with drainage systems is also critical.


 English
English Français
Français русский
русский Español
Español