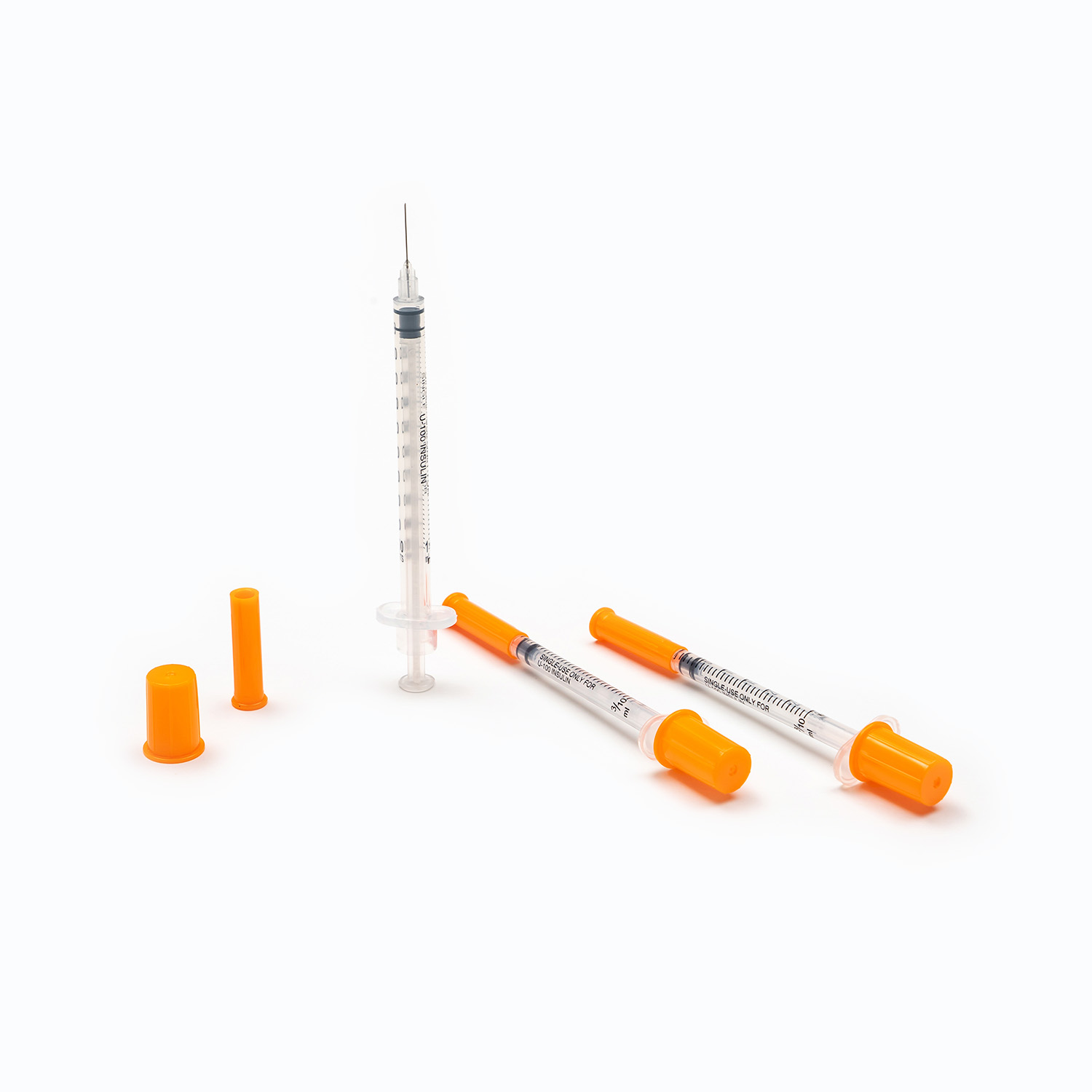
Insulin Syringe: A Key Tool in the Era of Precise Blood Sugar Control
Dec 08,2025
Introduction
In modern diabetes management, the insulin syringe has become an indispensable basic instrument for both clinical and home use. With the continuous updating of insulin treatment regimens, there are higher demands for the safety, comfort, and precision of injection tools. From medical materials to needle tip angle, from scale accuracy to injection experience, the insulin syringe carries far more complex medical value than its appearance suggests.
The Core Role of Insulin Syringes in Diabetes Management
The characteristics of insulin dictate that it cannot be taken orally, so injection is the most common method of administration. The design of the insulin syringe is based on in-depth research into the properties of insulin, subcutaneous tissue structure, and patient handling habits, ensuring that the drug is stably delivered to the subcutaneous fat layer and absorbed evenly. Whether it's the accurately adjusted dosage in medical institutions or the daily self-injections at home, the insulin syringe directly affects blood sugar fluctuations and the patient's trust in the treatment plan.
Increasing Demand and Individualized Care
Against the backdrop of long-term and increasingly individualized blood sugar control needs, the frequency of insulin syringe use is continuously increasing, driving continuous optimization in product structure, material technology, and safety design. Especially for patients using insulin for the first time, the ease of use of the injection tool often determines whether the treatment starts smoothly.
Precision Engineering and Optimized User Experience in Structural Design
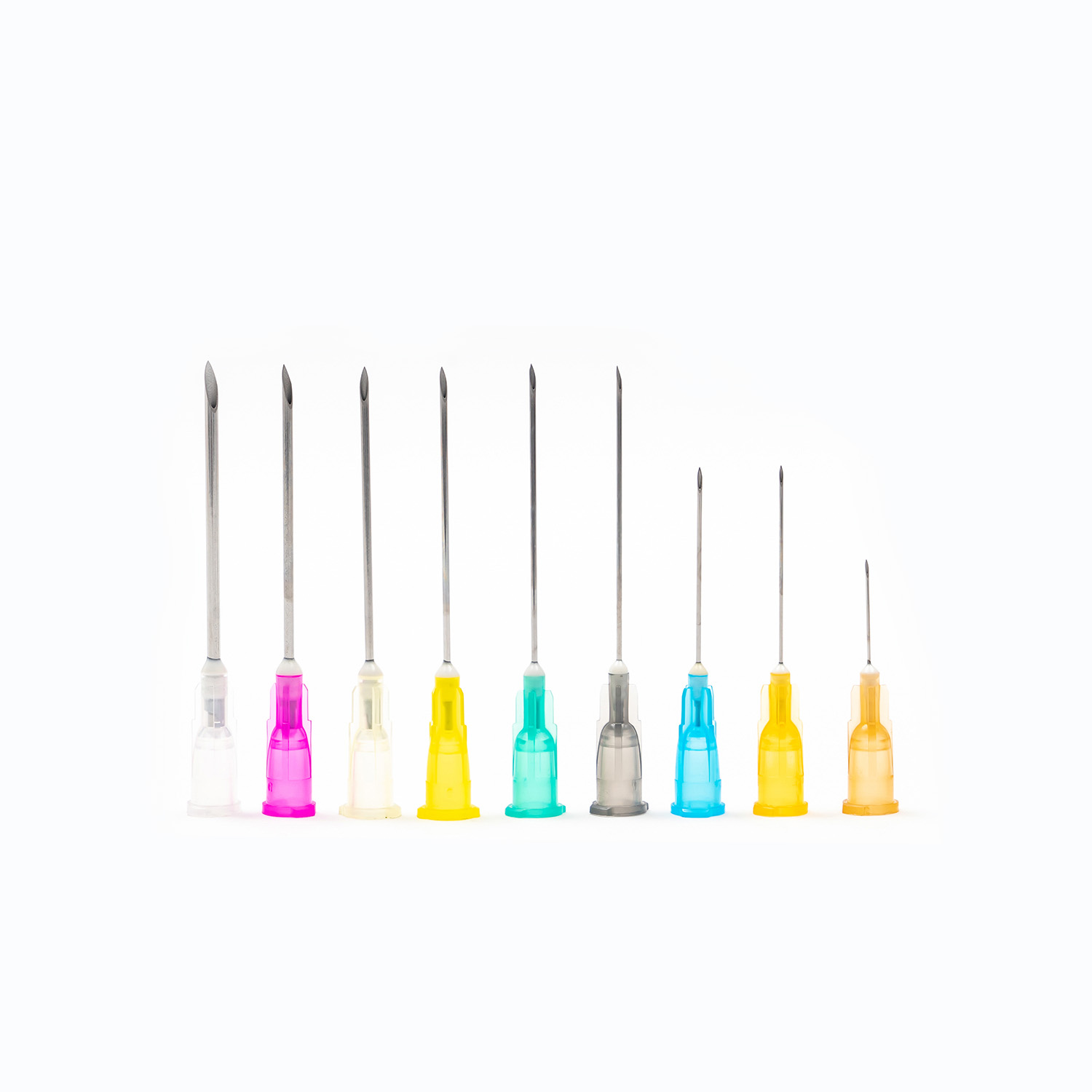
A seemingly ordinary insulin syringe actually embodies multiple micro-medical engineering concepts. The sharpness and angle of the needle tip directly affect the pain felt when piercing the skin; the transparency of the barrel and the clarity of the scale determine the accuracy of dose reading; and the resistance and airtightness of the plunger are closely related to the smoothness of injection. These factors collectively build the stability of the injection process and directly affect the uniformity of insulin distribution under the skin.
Needle and Barrel Dynamics
Modern manufacturing technology makes the needle body finer while maintaining sufficient strength to reduce patient discomfort during injection. The fit between the barrel and the plunger is also precisely calculated to make each injection more linear and stable, thereby reducing dosage errors caused by improper operation. With the advancement of biomaterial technology, more flexible and low-allergy materials are being used in syringes, improving safety while reducing skin irritation.

Material Advances and Mechanical Feedback
Biomaterial improvements allow for components that balance flexibility and durability, while mechanical refinements in plunger design provide smoother tactile feedback during injection. These combined refinements help maintain consistent delivery performance and improve the subjective experience of patients performing frequent injections.
Safety-Focused Design Drives Continuous Upgrades in Industry Standards
The safety of insulin syringes involves not only the materials themselves but also the proper procedures during use. The principle of single-use needles, the logic of rotating injection sites, and the sterile procedures required during dose withdrawal—these seemingly simple steps are crucial for the stability of long-term patient treatment. The industry is continuously upgrading product safety standards, leading to syringe designs that incorporate more protective features, such as structures that reduce the risk of needle-stick injuries and optimized internal designs to prevent insulin residue from causing dosage errors.
Waste Management and Post-Use Safety
With increasing emphasis on medical waste management, the market is gradually adopting designs that allow for safe needle enclosure, making it easier for patients to dispose of syringes at home and improving the overall safety of medical device disposal. For patients who require multiple daily injections over the long term, improved safety not only provides physical protection but also reduces psychological burden, making the treatment process more sustainable.
The Relationship Between Professional Usage Techniques and Long-Term Blood Sugar Control
Despite the continuous optimization of insulin syringe design, correct usage remains key to maintaining effective blood sugar control. Injection depth, angle, the steadiness of injection speed, and post-injection skin care all affect drug absorption. Through proper technique, insulin can diffuse more evenly under the skin, reducing the instability caused by blood sugar fluctuations.
Education and Skill Development
With the popularization of medical education, more patients are able to learn how to better use insulin syringes in their daily lives through professional guidance, such as mastering stable hand techniques during injection, maintaining good skin condition at the injection site, and avoiding repeated injections into hardened tissue. Improved professional usage skills not only reduce complications and discomfort but also increase confidence in the entire treatment system, making blood sugar control more manageable.
Technological Trends Shaping the Future of Insulin Syringes
The professional development of insulin syringes is closely linked to the progress of the diabetes treatment system. From precise drug delivery to long-term management, from safety design to user experience, it plays an irreplaceable role in improving patients' quality of life. As technology continues to advance, every improvement in syringes will drive more refined, individualized, and comfortable blood sugar control methods, bringing a more stable and predictable future to diabetes management.
Design Direction and Patient-Centered Development
Future directions emphasize ergonomic refinement, clearer visual guidance, and mechanical consistency to support sustained adherence to therapy. Innovations are increasingly focused on reducing physical discomfort while enhancing the reliability of dose delivery across varied real-world conditions.
The professional development of insulin syringes is closely linked to the progress of the diabetes treatment system. From precise drug delivery to long-term management, from safety design to user experience, it plays an irreplaceable role in improving patients' quality of life. As technology continues to advance, every improvement in syringes will drive more refined, individualized, and comfortable blood sugar control methods, bringing a more stable and predictable future to diabetes management.


 English
English Français
Français русский
русский Español
Español