What are the key quality indicators of Insulin Syringe in the procurement of medical consumables?
Feb 08,2026
An Insulin Syringe is a precision medical device designed for accurate subcutaneous delivery of insulin. For distributors, wholesalers, and medical supply importers, selecting the correct insulin syringe requires a clear understanding of structural design, material compatibility, dosing accuracy, and regulatory expectations. This guide provides an engineer-level overview to support professional procurement decisions.
What Is an Insulin Syringe and Why It Matters
An Insulin Syringe is specifically calibrated for insulin concentration and dosage accuracy. Unlike general-purpose syringes, insulin syringes are optimized to reduce dosing error, minimize patient discomfort, and ensure repeatable performance over long-term use, especially for insulin syringe for diabetic patients.
From a technical standpoint, insulin syringes differ in barrel graduation precision, needle geometry, and dead space control. These factors directly influence therapeutic outcomes and insulin waste.
| Parameter | Insulin Syringe | Standard Syringe |
| Graduation Accuracy | High precision for insulin units | General volume measurement |
| Needle Design | Ultra-fine, short bevel | General-purpose bevel |
| Dead Space | Optimized or low dead space | Higher residual volume |
Types of Insulin Syringes Available on the Market
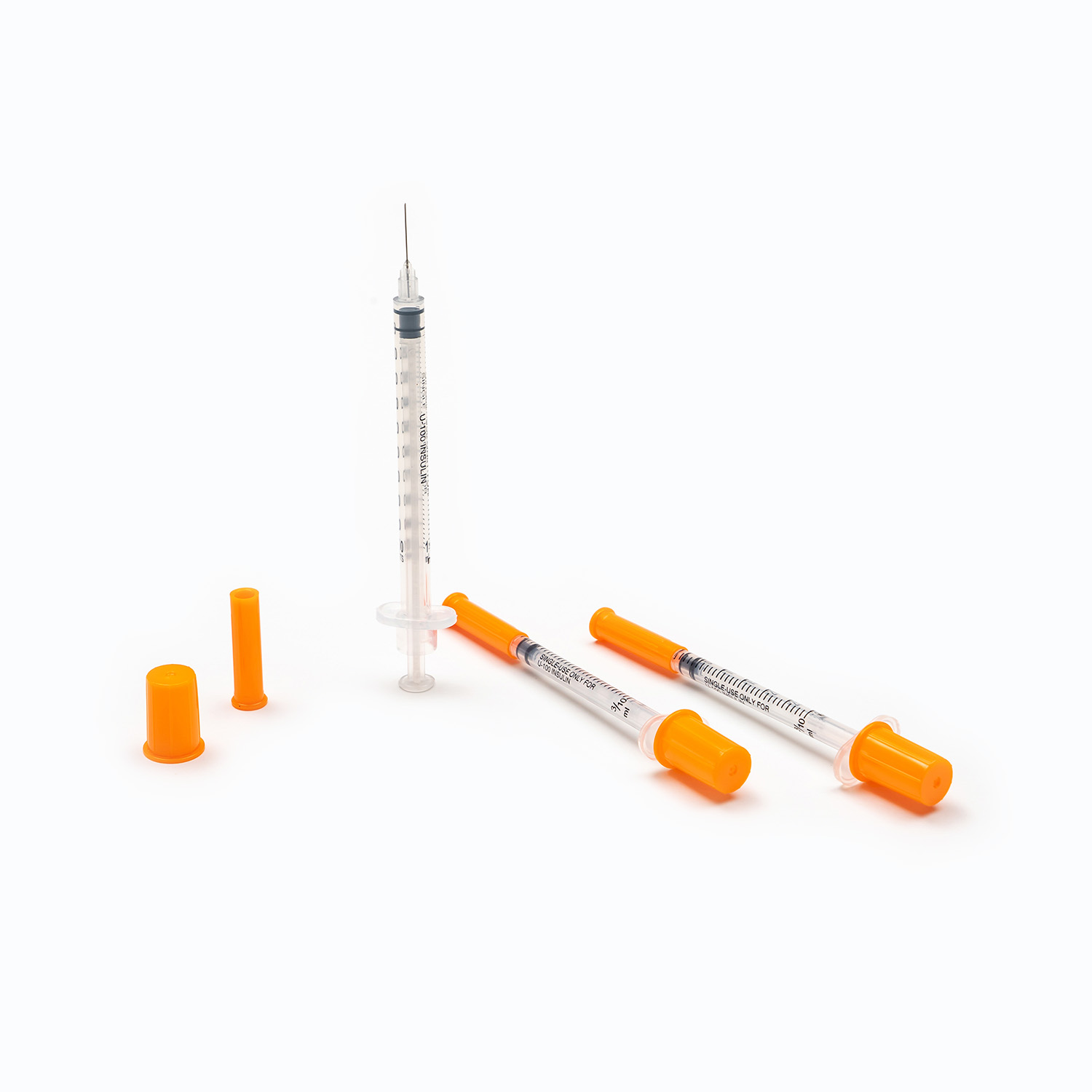
Disposable Insulin Syringe with Needle
A disposable insulin syringe with needle integrates the barrel, plunger, and needle into a single-use system. This configuration significantly reduces cross-contamination risk and eliminates assembly errors.
From a supply-chain perspective, disposable designs simplify inventory management and ensure compliance with infection control standards in both clinical and home-care environments.
| Feature | Disposable Syringe | Reusable Syringe |
| Hygiene Control | Excellent (single-use) | Dependent on sterilization |
| Operational Risk | Low | Moderate |
| Logistics Efficiency | High | Lower |
Low Dead Space Insulin Syringe
A low dead space insulin syringe is engineered to minimize the residual volume of insulin remaining in the needle hub and tip after injection.
This design is achieved through reduced hub geometry and tighter plunger-to-needle alignment, which can significantly reduce cumulative insulin loss over repeated injections.
| Design Aspect | Low Dead Space | Conventional Design |
| Residual Volume | Minimal | Higher |
| Insulin Waste | Reduced | Increased |
| Long-Term Cost Impact | Lower | Higher |
How to Choose the Right Insulin Syringe Size and Specification
Insulin Syringe 1ml 29G – Who Is It For?
The insulin syringe 1ml 29g configuration is widely adopted due to its balance between capacity, mechanical strength, and patient comfort.
A 1ml barrel supports higher-dose regimens, while a 29G needle offers sufficient rigidity with reduced insertion force compared to lower gauge needles.
| Specification | 1ml 29G | Smaller / Finer Options |
| Dose Capacity | High | Limited |
| Needle Strength | Balanced | Lower |
| User Adaptability | Wide range | Niche use |
Other Common Sizes and Gauge Options
Selecting the correct size and gauge depends on dosage frequency, viscosity, and user handling capability.
- 0.3ml syringes: optimized for low-dose precision
- 0.5ml syringes: mid-range dosing flexibility
- 30G–31G needles: reduced penetration force but higher flexibility
Insulin Syringe for Home Use – Safety and Convenience
An insulin syringe for home use must prioritize operational simplicity, clear scale visibility, and safe disposal compatibility.
Engineering considerations include ergonomic plunger force, anti-slip barrel surface, and consistent needle sharpness across production batches.
| Requirement | Home Use Priority | Clinical Priority |
| Ease of Handling | Very High | Moderate |
| Visual Clarity | Essential | Standard |
| Training Dependency | Low | Higher |
Who Should Use Insulin Syringes
Insulin syringe for diabetic patients remains the primary application, but procurement requirements vary across usage scenarios.
- Long-term insulin therapy patients
- Home healthcare programs
- Institutional medical supply distribution
Each segment places different emphasis on cost stability, specification consistency, and regulatory documentation.
Why Technical Quality Matters for Professional Procurement
For B2B buyers, insulin syringes must meet strict dimensional tolerance, material biocompatibility, and batch traceability standards.
Key engineering parameters include barrel roundness, plunger friction coefficient, and needle concentricity, all of which affect dosing accuracy and user experience.
- Consistent molding precision across cavities
- Medical-grade polymer compatibility
- Process-controlled needle grinding and polishing
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What makes an insulin syringe different from a regular syringe?
Insulin syringes are calibrated specifically for insulin dosing and feature optimized needle and dead space designs to ensure accuracy.
2. Why is low dead space important in insulin syringes?
Low dead space reduces residual insulin waste, improving dosing efficiency over long-term use.
3. Is a disposable insulin syringe with needle suitable for home use?
Yes, disposable designs offer higher safety and lower contamination risk for non-clinical environments.
4. How do I choose between different syringe sizes?
Selection depends on dosage volume, injection frequency, and user handling capability.
5. Why is the insulin syringe 1ml 29g commonly specified in bulk orders?
It provides a practical balance between capacity, comfort, and mechanical reliability.


 English
English Français
Français русский
русский Español
Español