Why High-Quality Blood Transfusion Sets Matter in Modern Healthcare?
Oct 15,2025
I. Understanding the Basic Concept of Blood Transfusion Set
1. What is a Blood Transfusion Set
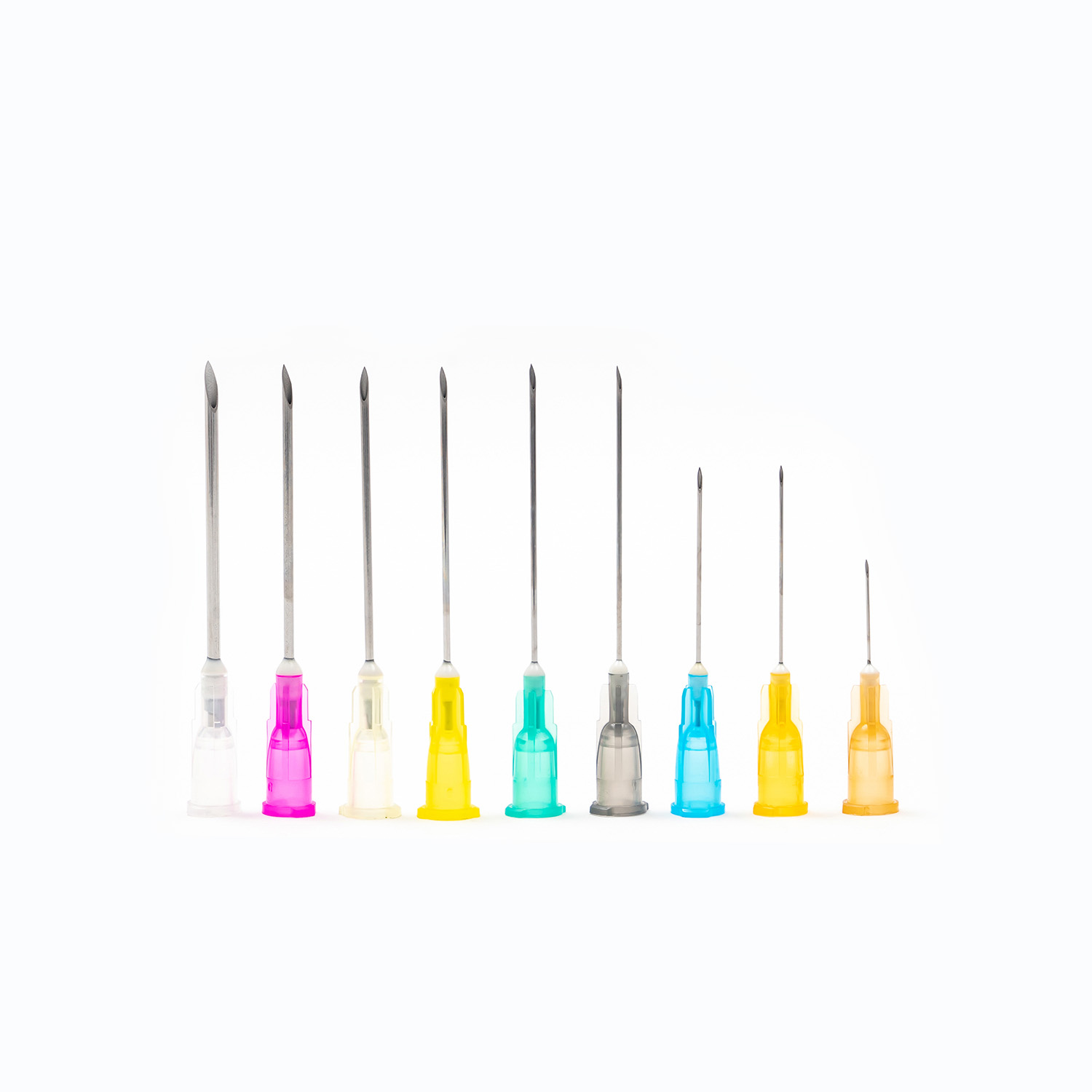
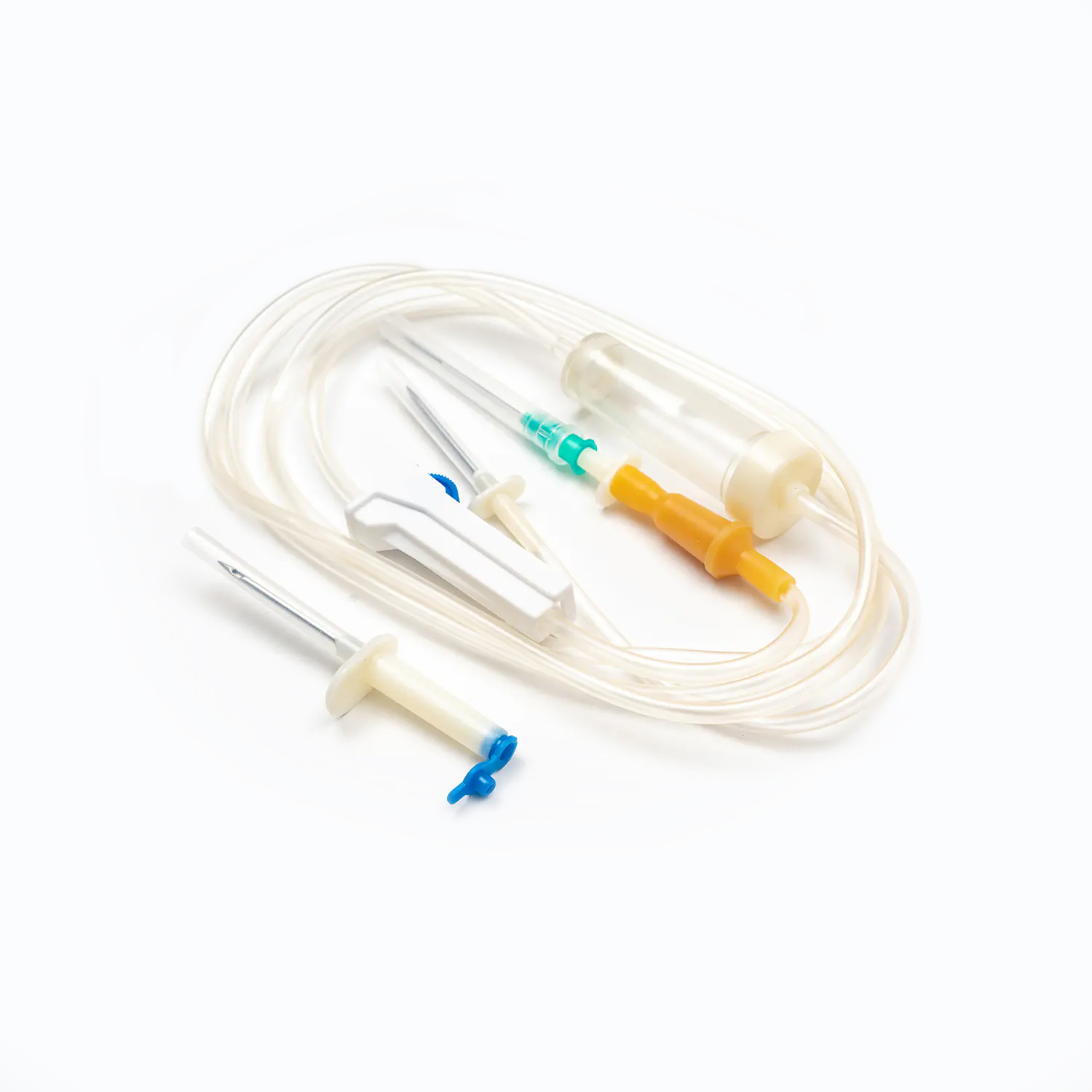
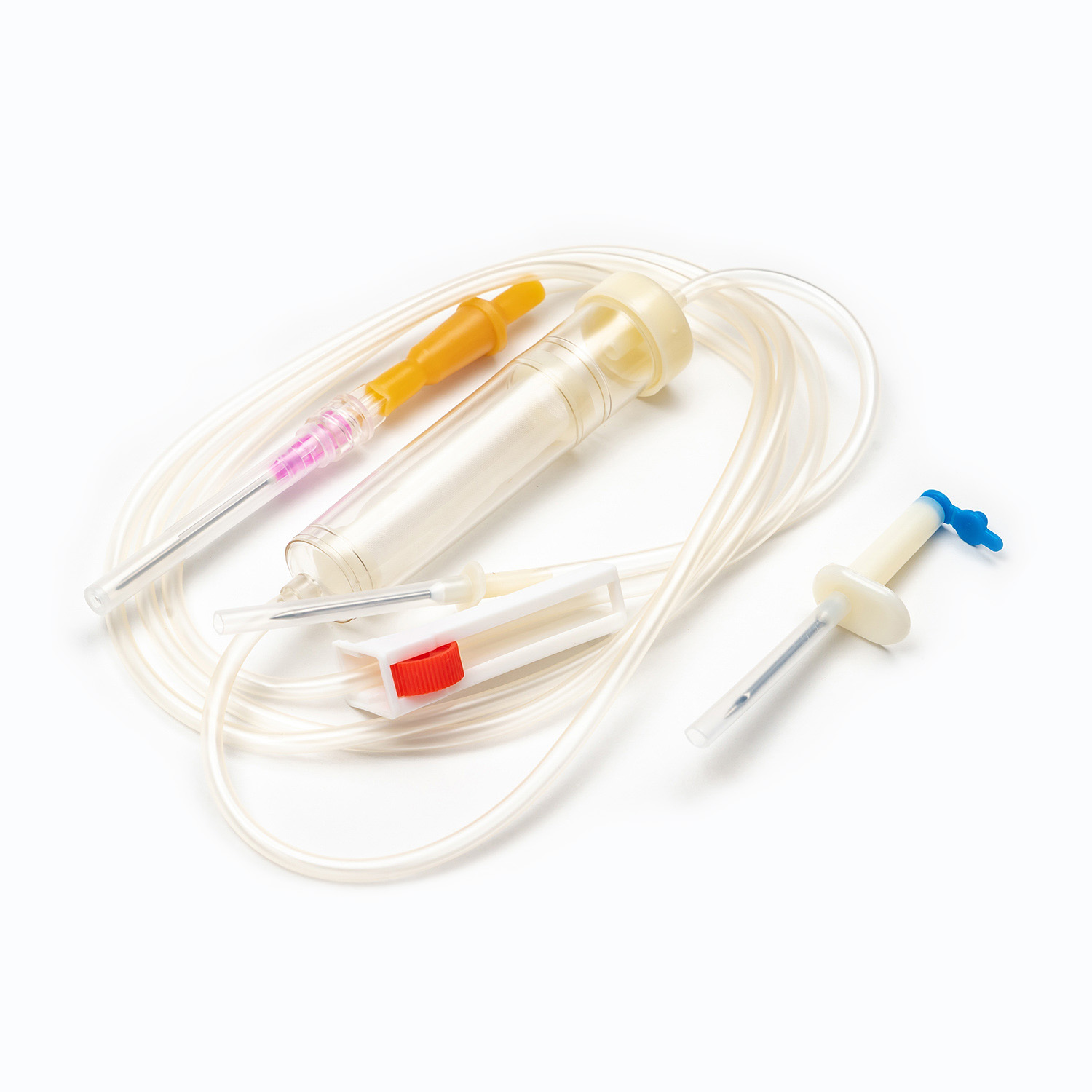
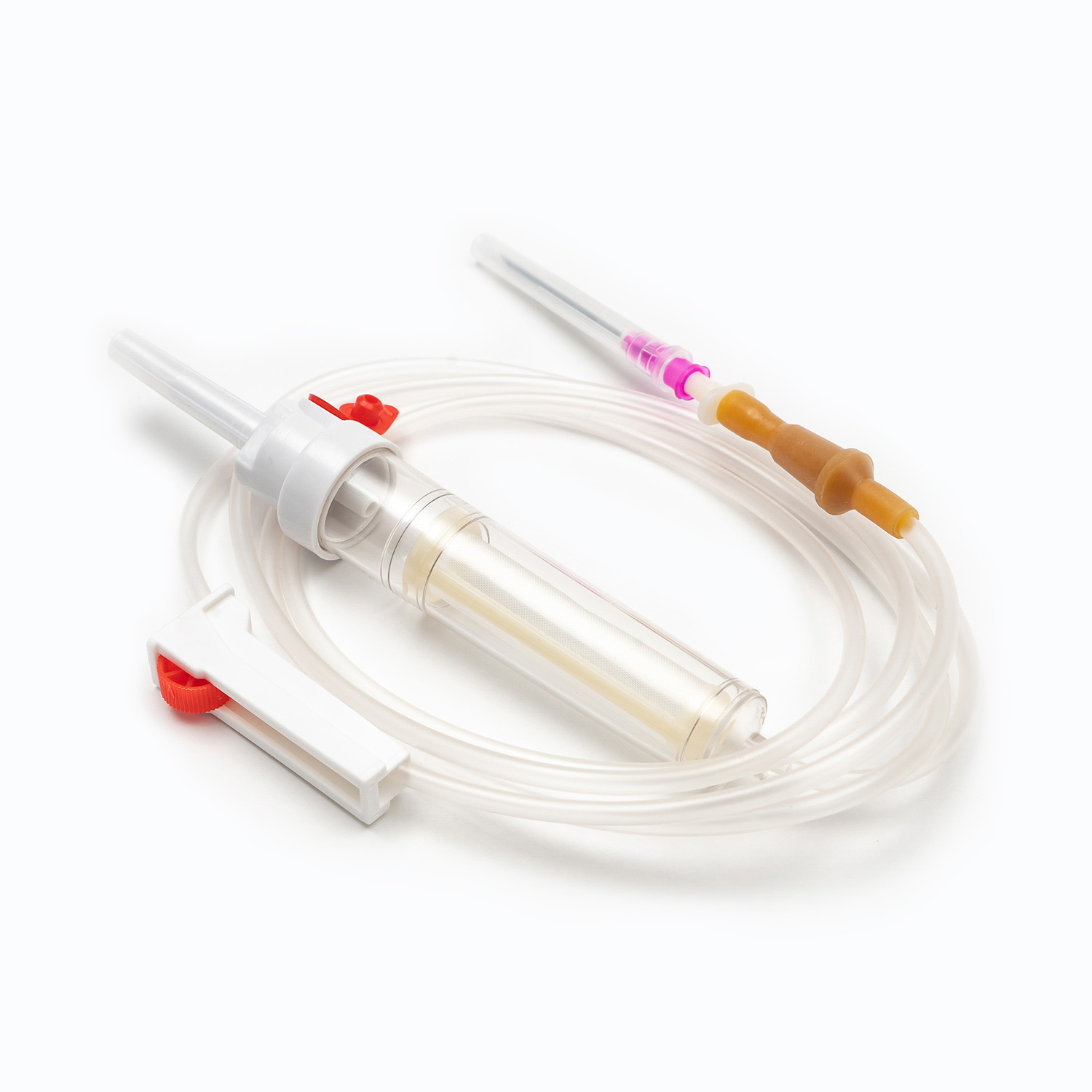
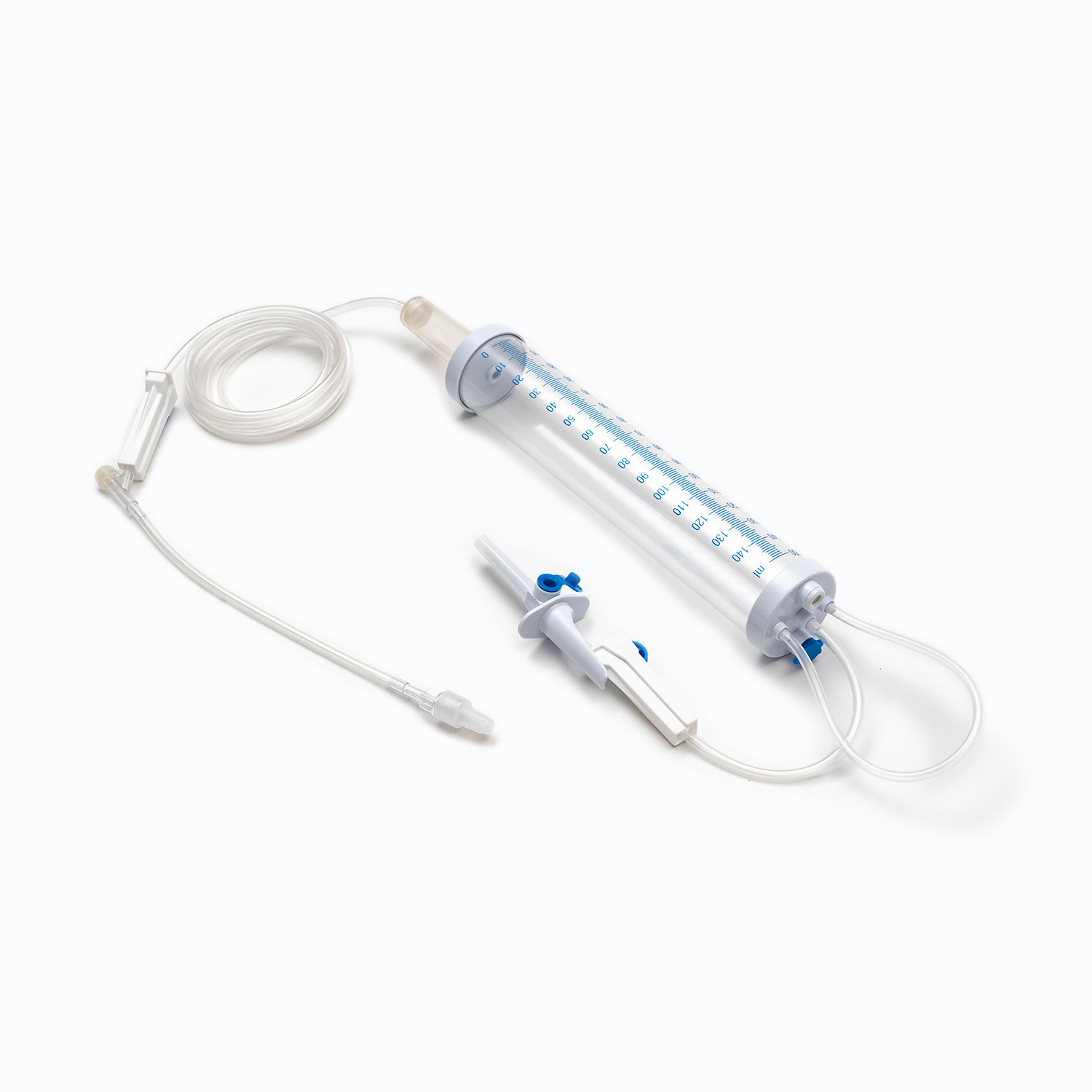
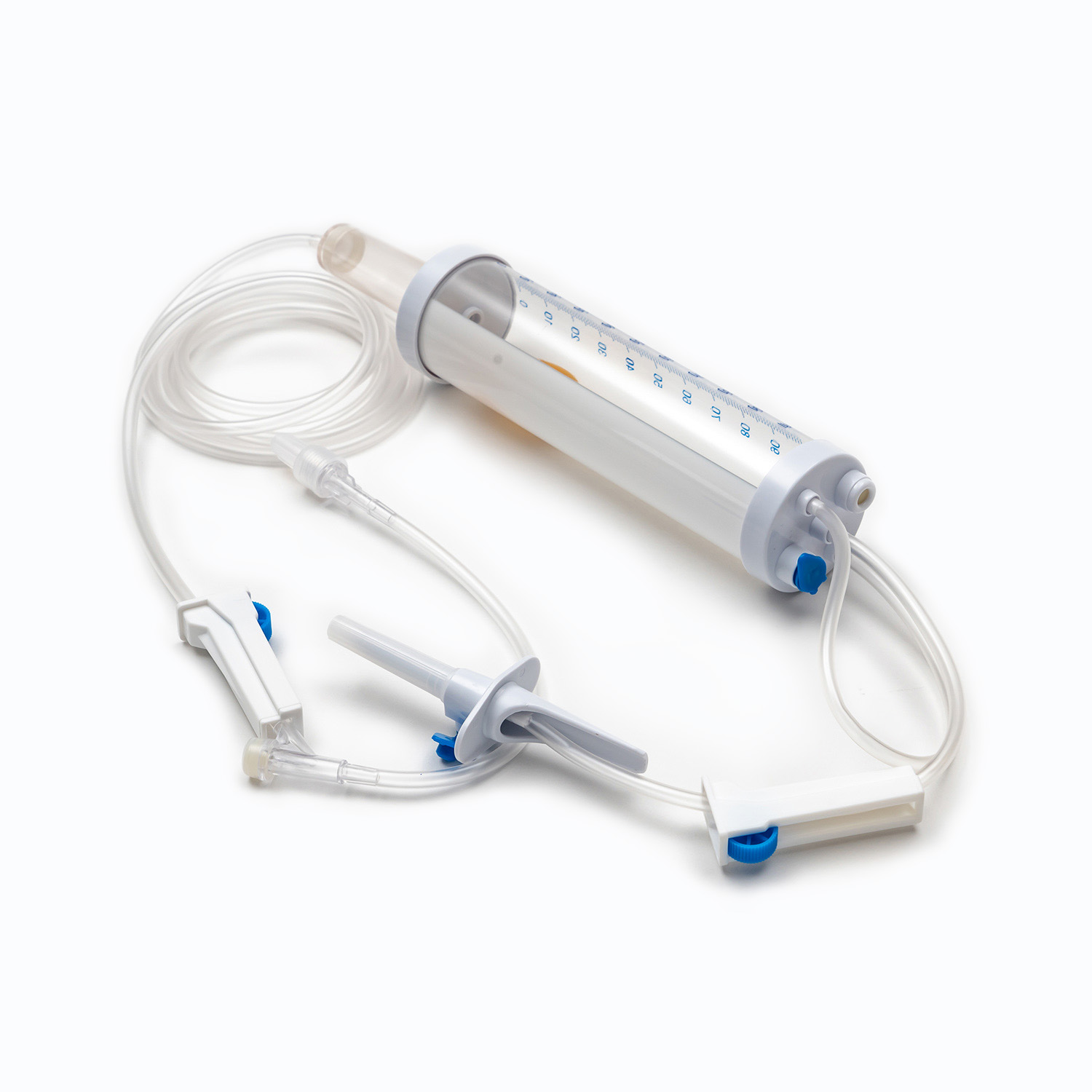
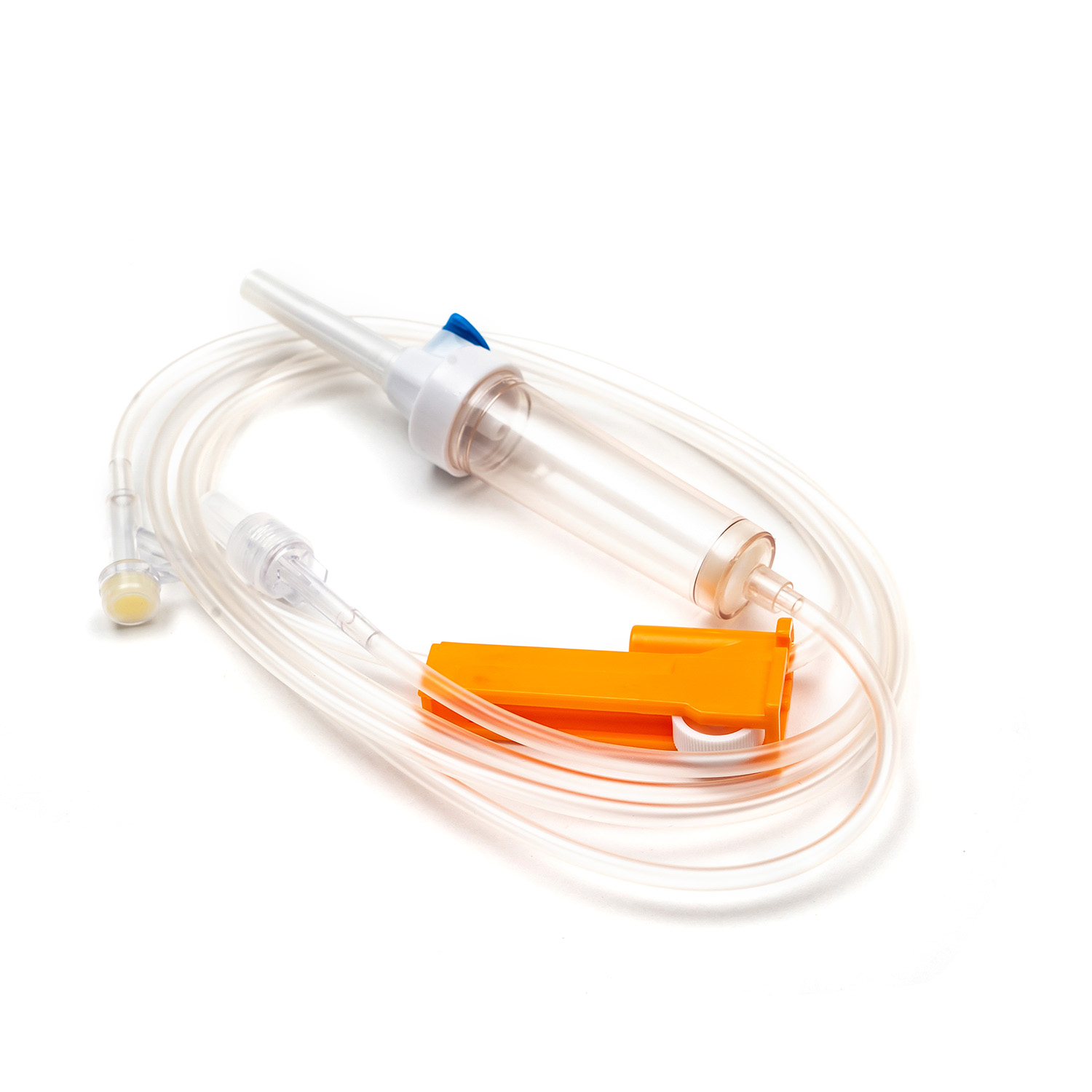
A Blood Transfusion Set is one of the most essential medical devices used in hospitals and clinical settings. It is designed to safely and accurately deliver blood or blood products from storage bags into a patient’s body. A complete transfusion set typically includes a transfusion needle, drip chamber, tubing, blood filter, flow regulator, and connectors, ensuring a sealed and controlled flow system during transfusion. Compared to a standard IV Infusion Set, the Blood Transfusion Set is more focused on maintaining blood stability and anti-coagulation properties while meeting strict sterility standards. Since blood is thicker and more complex than regular solutions, the transfusion set must feature excellent anti-blocking performance and precise flow control.
2. Working Principle of Blood Transfusion Set
Although it looks simple, the working principle of a transfusion set is delicate and precise. Through Medical Tubing and Needles, it connects the blood bag to the patient’s vein, maintaining a closed system that allows blood to flow by gravity or with the help of pressure. The process must remain sterile, steady, and fully controlled to avoid air embolism or excessive flow rate. Generally, there are two types of transfusion systems:
- Gravity type: Uses blood’s own gravity pressure for delivery.
- Pressure type: Uses external pressure devices for rapid transfusion in emergencies.
Regardless of the type, every system must be a Sterile Transfusion Equipment to ensure transfusion safety.
II. Key Components of a Blood Transfusion Set
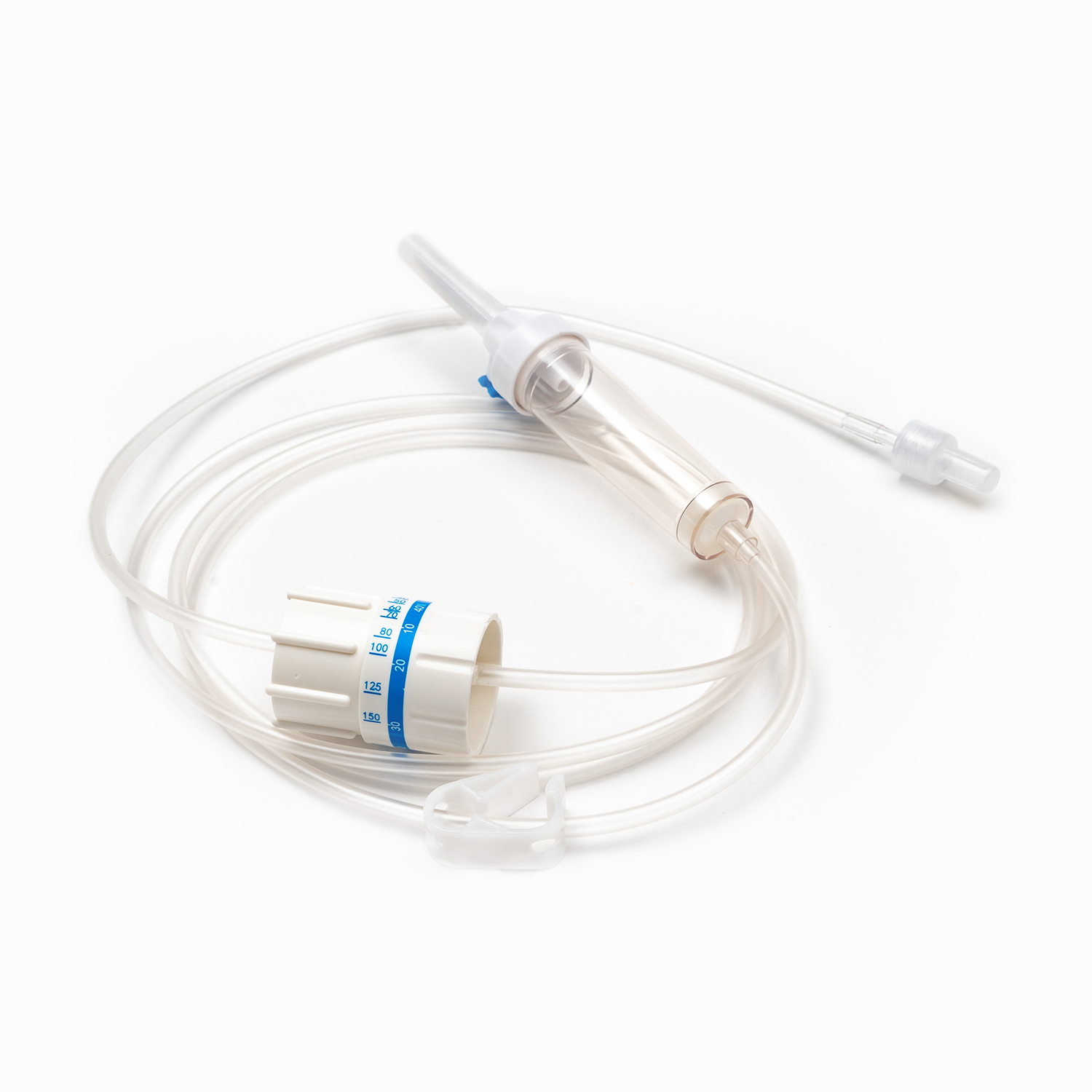
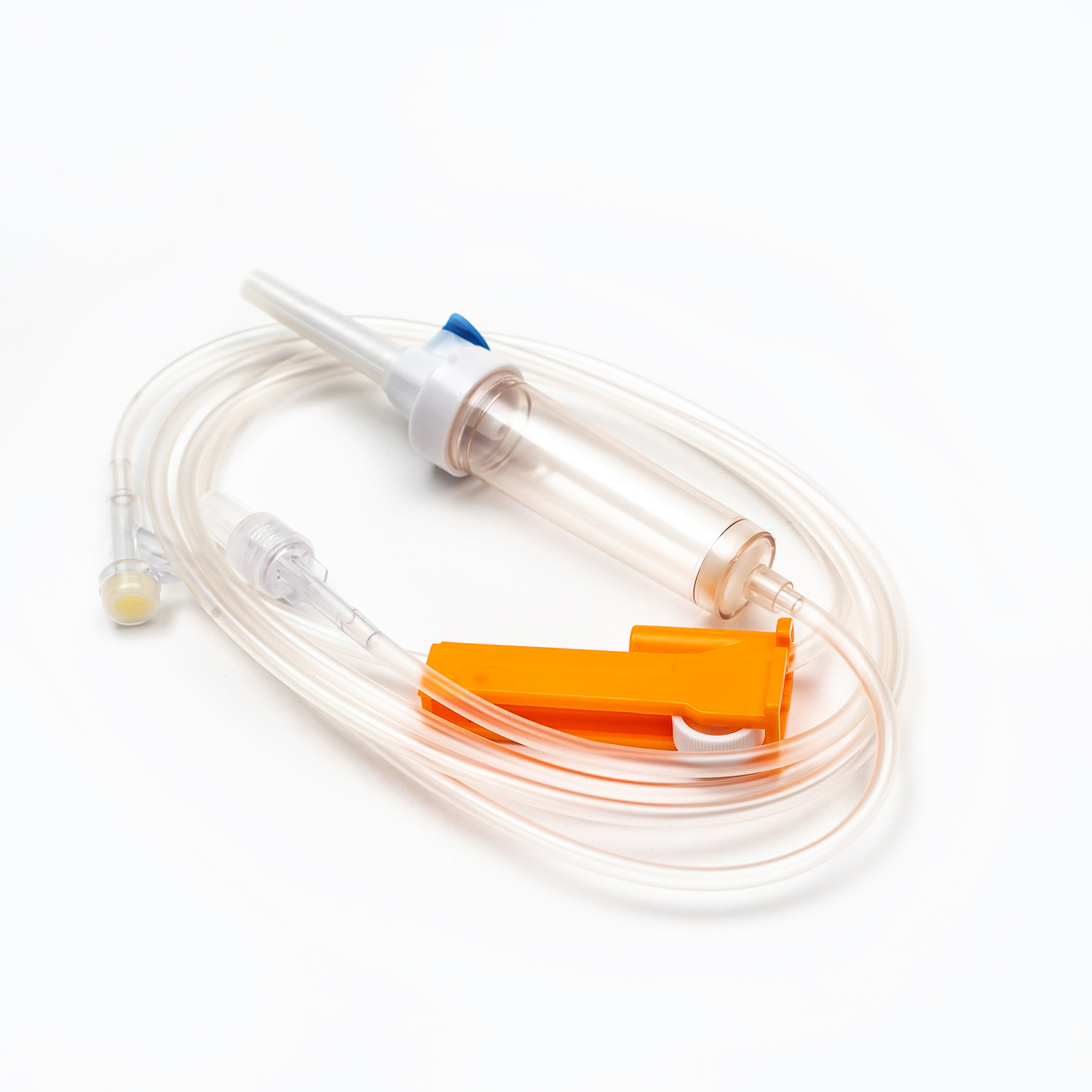
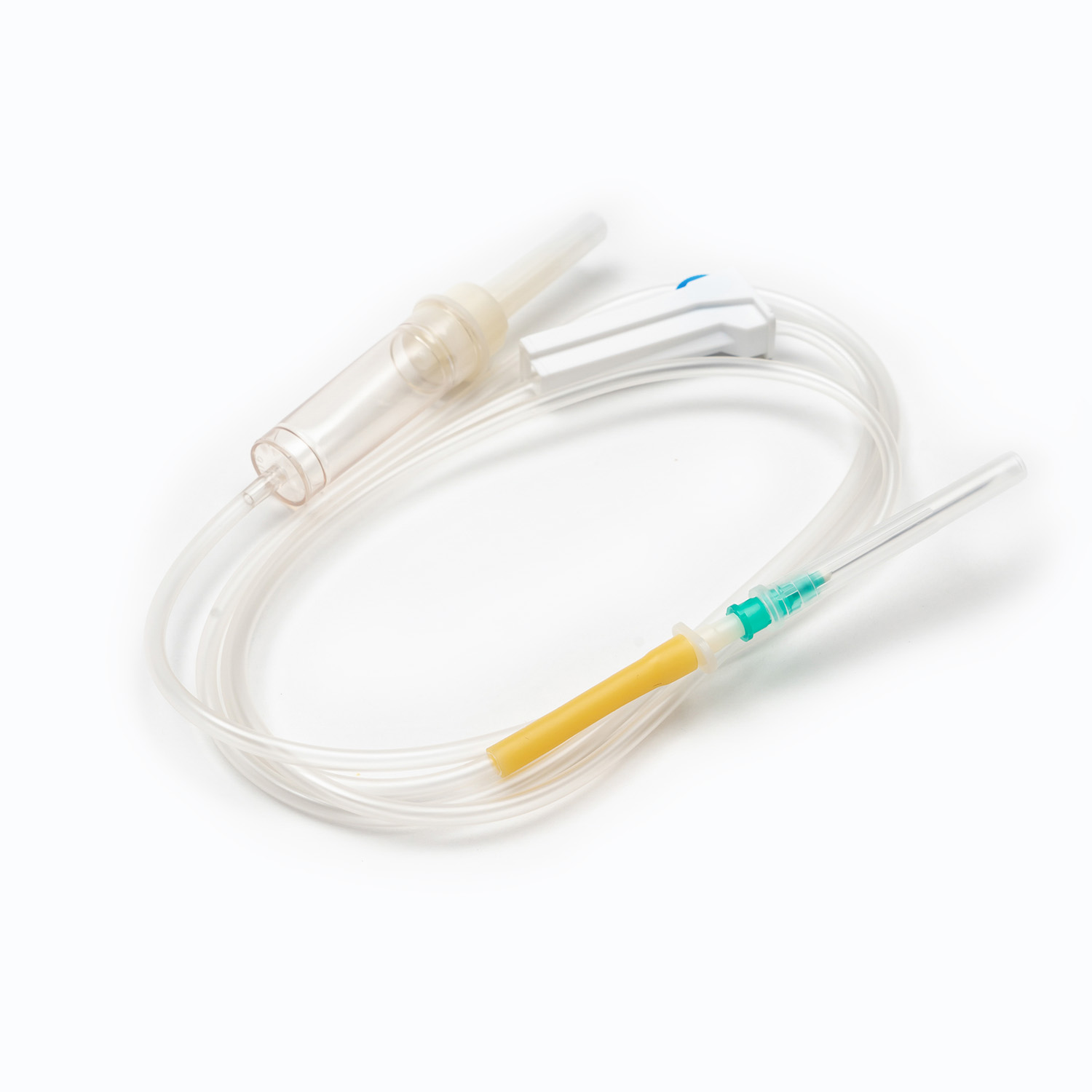
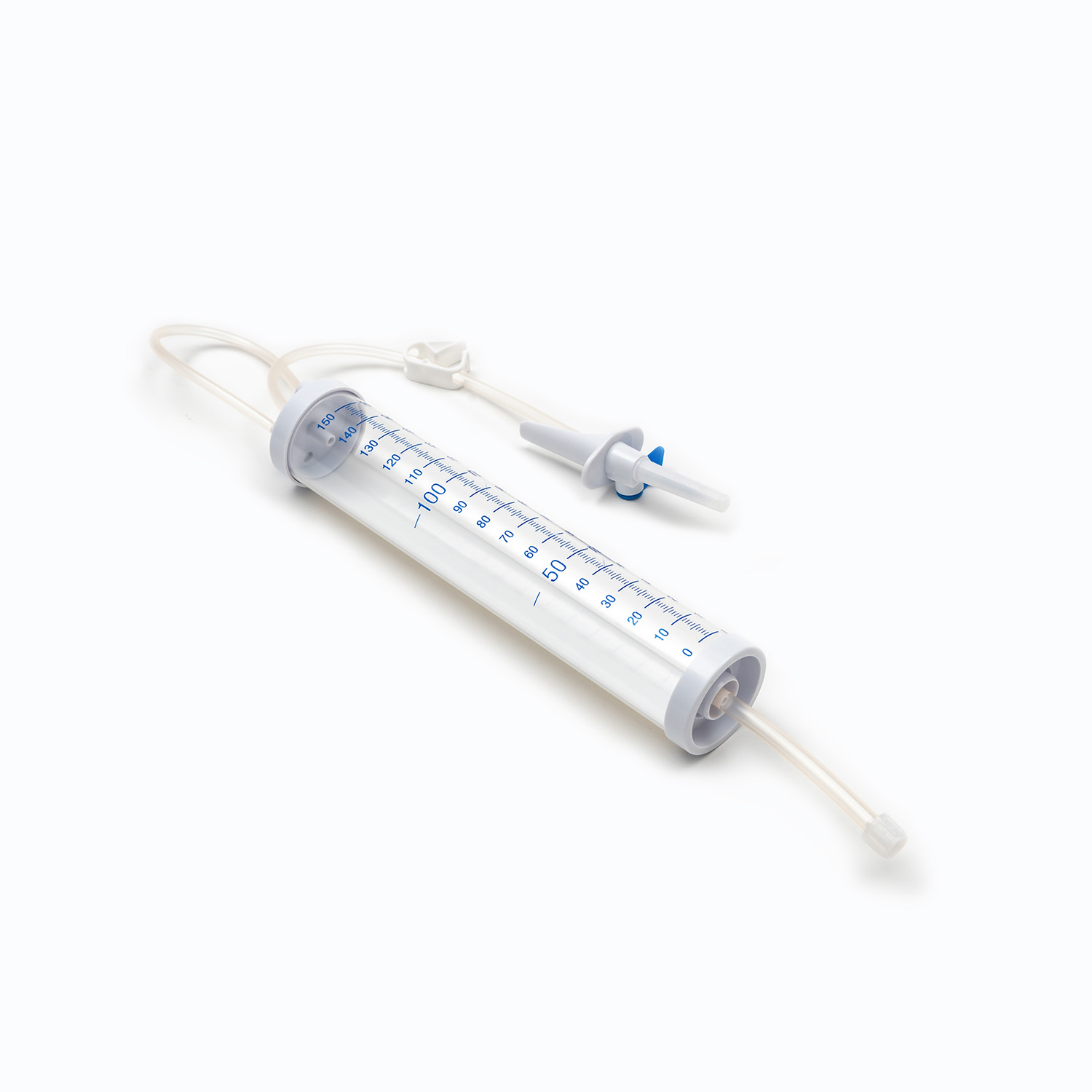
1. Drip Chamber and Filter
The drip chamber is a vital part of the Blood Transfusion Set. It allows medical staff to observe the drop rate while preventing air bubbles from entering. The built-in filter removes clots and impurities to protect the patient’s veins. High-quality filters are usually made of medical-grade nylon or stainless steel mesh with pore sizes below 200 microns.
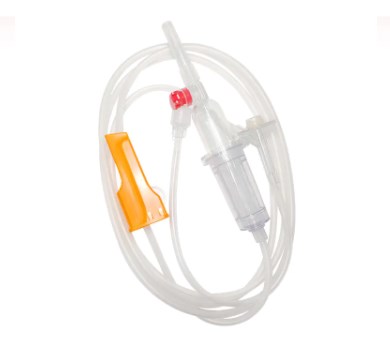
2. Tubing and Flow Regulator
The tubing of Medical Tubing and Needles is typically made of PVC or DEHP-free materials that ensure flexibility and biocompatibility. The flow regulator helps precisely control the blood flow rate, allowing each drop to enter the body evenly without causing pressure imbalance.
3. Connection Needle and Air Filter System
The connecting needle has two ends — one connects to the blood bag, the other to the transfusion needle or cannula. Modern transfusion sets often feature air filters to prevent air from mixing into the blood flow, effectively reducing the risk of air embolism.
4. Sterile Packaging and Disposable Use
Almost all transfusion sets today are Disposable Medical Devices, sterilized with ethylene oxide (EO) or gamma radiation. These single-use devices eliminate cross-contamination risks and simplify the workflow for healthcare providers.
III. Classification and Applications of Blood Transfusion Sets
1. By Structure
- With air vent: For glass containers or systems requiring pressure balance.
- Without air vent: For flexible blood bags to maintain a closed system.
- With filter: For filtering blood clots and particles.
- Without filter: For pre-filtered blood products.
2. By Patient Type
- Adult type: For standard surgeries and emergency transfusion.
- Pediatric type: For precise low-flow control in children.
- Special-purpose type: For neonatal exchange or plasma separation.
3. By Delivery Method
- Gravity system: For routine transfusion.
- Pressure system: Works with a Blood Administration System for rapid blood delivery.
IV. Clinical Use of Blood Transfusion Set
1. Preparation
Before transfusion, medical staff must inspect the blood bag’s integrity, expiration date, and blood type. The packaging of the Blood Transfusion Set must be intact with no leaks or damage before opening.
2. Connection and Air Removal
After opening, insert the needle into the blood bag outlet and hang the bag on a stand. Fill the drip chamber partially to remove air, then expel all bubbles from the tubing to ensure a completely filled line.
3. Transfusion Operation
Insert the needle or cannula into the patient’s vein, adjust the flow rate (usually 40–60 drops per minute), and closely monitor the patient’s reaction. If any adverse symptoms appear, the transfusion must be stopped immediately.
4. Disposal
After transfusion, close the regulator, remove the needle, and dispose of the entire Blood Transfusion Set and bag in medical waste containers according to regulations.
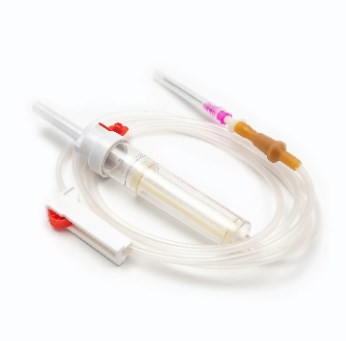
V. Difference Between Blood Transfusion Set and IV Infusion Set
Although similar in appearance, the IV Infusion Set and Blood Transfusion Set differ greatly in purpose and performance.
1. Function
The IV Infusion Set is for delivering fluids or medications, while the Blood Transfusion Set is specifically designed for blood and blood products.
2. Material and Standards
Transfusion sets use non-toxic, DEHP-free, and biocompatible materials to ensure blood compatibility and comply with ISO 3826 and EN ISO 8536 standards.
3. Flow Control
Blood transfusion sets have precision regulators and filters to maintain stable flow, even for viscous fluids like blood.
VI. Advantages of Using High-Quality Blood Transfusion Sets
1. Safety and Sterility
A Sterile Transfusion Equipment ensures that blood is transferred under aseptic conditions. Using Disposable Medical Devices prevents cross-contamination and simplifies medical operations.
2. Precise and Stable Flow Control
High-quality sets are engineered for accurate flow regulation (0–120 drops/min), critical during major surgeries or emergency transfusions.
3. Convenience and Compatibility
Modern Medical Tubing and Needles are flexible, kink-resistant, and easy to connect. Some sets integrate directly with Blood Administration Systems for faster, safer transfusions.
4. Versatility
Different models meet different clinical needs:
- Emergency: pressure transfusion sets.
- Pediatrics: micro-drip sets.
- Operating rooms: anti-bubble transparent sets.
VII. Applications in Modern Healthcare
1. Hospitals and Clinics
In hospital transfusion centers, Blood Transfusion Sets are vital for delivering red cells, plasma, and platelets. Advanced Blood Administration Systems now allow automated control and digital monitoring for added safety.
2. Emergency and Field Medicine
Portable and disposable sets are indispensable in disaster relief, military, and field hospitals. Pressure-type sets enable rapid transfusions in life-threatening situations.
3. Research and Training
Transfusion sets are also used in research labs and medical training programs for testing flow rate, filtration performance, and equipment compatibility.
VIII. Maintenance, Storage, and Disposal
1. Storage Conditions
Although Disposable Medical Devices, transfusion sets must be stored at 10–30°C, humidity below 80%, and away from direct sunlight to prevent material degradation.
2. Inspection Before Use
Before use, inspect packaging, expiration date, and integrity. Any damaged or contaminated device must be discarded immediately.
3. Waste Management
Used transfusion sets are classified as infectious medical waste. They must be disposed of in dedicated containers and treated under high temperature or specialized waste systems.
IX. Technological Innovation and Future Trends
1. Intelligent Blood Administration Systems
Future Blood Administration Systems will integrate IoT technology, RFID blood bag tracking, and real-time monitoring to achieve traceable and automated transfusion control.
2. Sustainable and Eco-Friendly Design
Next-generation Blood Transfusion Sets will utilize biodegradable materials like PLA and bio-based polymers to reduce medical waste and support sustainability.
3. Advanced Filtration and Anti-Bubble Technology
Upcoming designs will feature nano-scale filters for better impurity and air removal, reducing transfusion-related complications.
4. Standardization and Global Market Growth
International standardization (ISO, WHO) ensures compatibility and traceability worldwide. Emerging markets in Asia and Africa show rapid growth in demand for cost-effective, high-quality transfusion sets.
X. Conclusion
The Blood Transfusion Set plays a vital role in modern healthcare, ensuring safe and efficient blood delivery. From traditional glass tube designs to today’s intelligent and sterile systems, its evolution reflects the progress of medical technology and the pursuit of patient safety. With advancements in automation, environmental sustainability, and precision control, future transfusion sets will become smarter and safer. Whether in hospitals, ambulances, or field clinics, they will continue to safeguard lives and support


 English
English Français
Français русский
русский Español
Español